What Is Keyword Cannibalization?
Keyword cannibalization happens when two or more pages on your website target the same keywords and search intent. This causes them to compete for rankings on Google. As a result, Google decides which page to rank higher, and it might not be the page you want to prioritize. This competition can hurt your site’s organic traffic overall.
Cannibalization occurs when two or more pages share the same search intent. To check for this, you need to understand the purpose of each page. Sometimes, having similar keywords on different pages is okay if their intent is distinct.
For example, one page might provide information about a product, while another focuses on selling it (like a product page). In this case, both pages serve different purposes in the buyer’s journey, so there’s no need to worry about cannibalization.
But, if two pages target similar keywords and have the same intent, they will compete with each other for the same audience. That’s when keyword cannibalization becomes an issue.
Why Is Keyword Cannibalization Bad for SEO?
This internal competition can negatively impact SEO in several ways:
1. Reduced Page Authority
When multiple pages on a website target the same keyword, they end up competing against each other for search engine rankings. This competition splits the page authority—measured by factors like backlinks and content quality—across several pages instead of consolidating it into one authoritative page.
As a result, each page has less authority, making it harder for any single page to rank well in search results. Consolidating these pages into one comprehensive page can help concentrate authority and improve rankings.
2. Diluted Link Equity
Keyword cannibalization also harms your SEO by spreading out your link equity. Backlinks, which boost a page’s SEO, lose their impact when they’re divided among multiple pages targeting the same keyword.
Instead of all the backlinks strengthening one powerful page, they get split, reducing their overall authority. This makes it harder for any of the pages to rank high, while a single, focused page could have performed much better in search results.
3. Competing With Yourself
If you spread your keywords across several pages, those pages end up competing with each other for rankings on search results. This competition often splits your organic traffic, meaning you’re likely getting less traffic than you could.
A Moz study in 2014 showed that 71.33% of search clicks go to results on the first page, white pages two and three only get 5.59% of clicks.
On top of that, the top five results on the first page grab 67.60% of total clicks, while positions 6 to 10 get just 3.73%. Having one high-ranking page is far better than multiple lower-ranking ones.
How to Identify Content Cannibalization at Scale
Finding keyword cannibalization needs a mix of SEO tools and some hands-on checking. Here’s how to do it:
1. Perform a Site Search
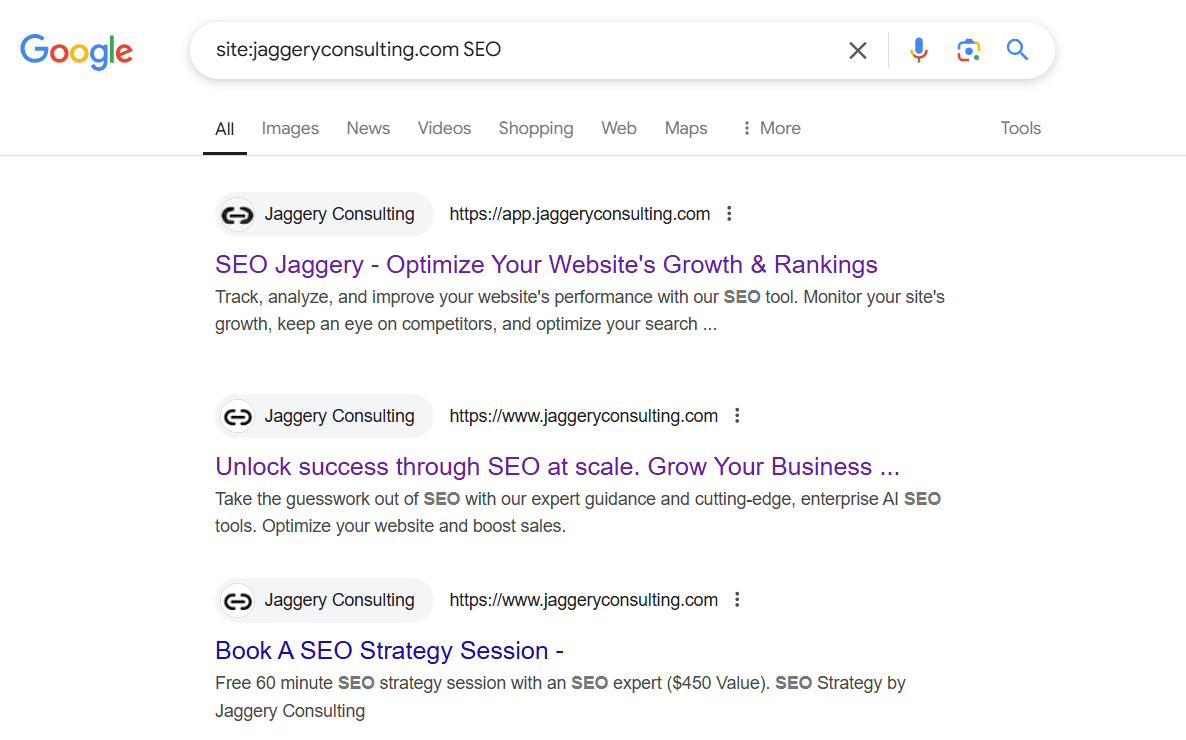
Using the site: operator in Google search is an easy way to find content cannibalization on your website. To use it, type site:yourdomain.com "keyword" in the Google search bar. This shows all pages on your site that include the keyword. It helps identify if multiple pages are targeting the same term, which can confuse search engines.
Let’s say your website is example.com, and you want to check for cannibalization on the keyword "healthy recipes." You would enter the site:example.com "SEO" into Google. If the search results show several different pages from your site focusing on "SEO," it indicates that these pages might be competing against each other in search engine rankings for the same keyword.
Here's what we see when we search for site:jaggeryconsulting.com SEO:
However, JaggeryConsulting has several pages ranking for ‘SEO,’ but each one serves a different purpose and targets unique search intents, so there’s no cannibalization happening.
This internal competition can dilute the authority of each page, making it harder for any single page to rank well.
2. Identifying with Google Search Console
To identify content cannibalization using Google Search Console (GSC), log in and go to the "Search results" option in the left menu.
Scroll down to find "Queries." This section shows the search terms people use to find your site and how many impressions and clicks you’ve received for each.
Click on any search term, then switch to the "Pages" tab. Here, you’ll see all the pages on your site that Google has shown for that term. If multiple pages appear for one search term, it could mean keyword cannibalization.
However, if Google shows sitelinks for your site, having multiple pages appear for one keyword doesn’t always indicate a problem. To confirm, search the keyword on Google and check how your pages appear.
3. Analyze Keyword Rankings
To spot content cannibalization, you can track how different pages rank for the same keyword over time. For example, if two blog posts on your website compete for the keyword "best investment strategies," they may keep switching positions in search results. This competition confuses search engines and splits your website's authority, potentially lowering your overall ranking.
For example, let’s say your website "xyz" offers SEO services, and two blog posts—"SEO Basics for Beginners" and "Simple SEO Tips"—target the keyword "SEO strategies."
Using our JaggeryConsulting tool can help you notice that both pages alternate between ranking at positions 8 and 12. This competition between your own pages can dilute your overall ranking potential.
Effective Strategies to Fix Content Cannibalization
Now that you know how to spot keyword cannibalization, it’s time to fix it. Thankfully, there are several simple strategies you can use to tackle these issues and protect your site’s SEO.
1. Content Consolidation
The best way to fix content cannibalization is by merging similar pages. If you have two or more weak pages competing for the same keywords and traffic, combining them into one stronger page is a smart move. This works especially well when one page performs better than the others.
By merging content, you reduce keyword competition and improve the SEO and quality of the combined page. It also boosts organic traffic and gives you a chance to update and expand your content.
Consolidating pages is a great way to not only fix cannibalization but also create fresh, valuable content.
If merging isn’t ideal, you can choose to remove low-quality pages instead. Just make sure to use 301 redirects to direct traffic from deleted pages to the right one. Also, update your internal links so they don’t point to pages that no longer exist. Let’s discuss this in details.
2. 301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a way to permanently send users and search engines from one URL to another. It's like setting up a change-of-address notice for your website, ensuring that anyone trying to visit an old page is automatically taken to the new one. This helps maintain a smooth user experience and preserves the page's search engine rankings.
For example, imagine you have a webpage at http://www.example.com/old-page that you've moved to http://www.example.com/new-page. By setting up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one, anyone who tries to visit the old page will be automatically redirected to the new page. This way, visitors won't encounter a "Page Not Found" error, and any existing links to the old page will still work seamlessly.
Implementing a 301 redirect is typically done by adding specific rules to your website's server configuration. For instance, on an Apache server, you can add the following line to your .htaccess file:
Redirect 301 /old-page http://www.example.com/new-page
This line tells the server that the old page is now permanently at a new URL, so all traffic and SEO value go to the right place.
3. Internal Linking Optimization
Optimizing internal links on your website ensures clear navigation for both users and search engines. Internal links connect your web pages, creating a structure that makes it easier for search engines to understand the importance of each page.
When multiple pages compete for the same keyword, redirecting internal links toward the primary page ensures that it receives more ranking authority.
To implement this strategy, perform these simple things:
- Identify which page should rank highest for a specific keyword.
- Review your website to locate internal links that point to other competing pages.
- Adjust those links so they direct traffic and authority to the chosen primary page.
- Make sure to use precise and relevant anchor text to enhance clarity for search engines and users alike.
Conduct regular reviews of your internal link structure to maintain its effectiveness. A well-organized internal linking system ensures that users can easily navigate your site, while search engines prioritize your most important pages for rankings. This simple adjustment can significantly improve both user experience and SEO performance.
4. Deoptimize Cannibals
You don’t always need to delete a page or its content to stop it from competing with another page for the same keywords. A simpler option is to deoptimize the competing page. This means removing the overlapping keywords from that page so it no longer ranks for them, eliminating the competition.
How to Decide Which Page to Deoptimize?
Focus on search intent. For example, let’s say you have two pages:
- “Top 28 SEO Tools for Shopify (+5 Bonus)”
- “199 point SEO checklist to up your SEO game.”
Both rank for the keyword “SEO.” Even though both are valuable, it may be better to deoptimize the first one. Why? Because the second page better matches broader search intent and provides a more detailed answer.
Deoptimizing the first page also gives you the chance to re-optimize it with new, more suitable keywords. Use this opportunity to do keyword research and find terms that better fit the page’s focus.
5. Use Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are HTML elements that help search engines identify the preferred version of a webpage when multiple pages have similar or identical content.
So, by specifying a canonical URL, webmasters can prevent duplicate content issues, ensuring that search engines index and rank the correct page. This practice consolidates link equity and improves the overall SEO performance of a website.
For example, consider an e-commerce website that offers the same product in different colors, each accessible through unique URLs:
- https://example.com/product?color=red
- https://example.com/product?color=blue
- https://example.com/product?color=green
Although these URLs lead to pages with similar content, search engines might view them as separate pages, potentially causing duplicate content issues. To address this, a canonical tag can be added to each variant's HTML code, pointing to the main product page:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/product">
This tag informs search engines that the primary version of the page is https://example.com/product, consolidating the ranking signals from all variants to this single URL.
Implementing canonical tags correctly is crucial for effective SEO. Common mistakes to avoid include using relative URLs instead of absolute ones, pointing canonical tags to non-existent pages, or having multiple canonical tags on a single page. Such errors can confuse search engines, leading to improper indexing and potential ranking issues.
6. Revising On-Page SEO
Revising on-page SEO means updating things like title tags, meta descriptions, and headers so every page targets different keywords and meets specific user needs. When multiple pages use the same keywords without being distinct, they end up competing with each other in search rankings. This competition confuses search engines about which page to show, which can lower the visibility of all those pages.
To fix this, review your website content to find pages with similar topics or keywords. For each page, create unique title tags that match the content, write clear meta descriptions that explain its specific value, and structure headers to align with its main keywords.
These changes help search engines understand each page’s purpose, making it easier to rank them correctly.
This approach not only improves search engine rankings but also makes it easier for visitors to find what they need. When users see content that matches their search, they stay engaged and feel more satisfied.
7. Content pruning
Content pruning is the process of removing or updating outdated, irrelevant, or low-quality content from your website to enhance its overall quality and performance. Think of it as decluttering your website to ensure visitors find only valuable and up-to-date information. Removing unnecessary content helps make the site easier to use and more attractive to both users and search engines.
Implementing content pruning offers several benefits:
- Improved SEO Performance: Search engines favor websites with high-quality, relevant content.
- Enhanced User Experience: Visitors can navigate your site more easily, finding the information they need without sifting through outdated or redundant content.
- Optimized Crawl Efficiency: Search engine bots can index your site more effectively, focusing on your most important pages.
To effectively prune your content, start by conducting a comprehensive content audit. This involves evaluating each page's performance metrics, such as traffic, engagement, and relevance to your current business goals.
Based on this assessment, decide whether to update, consolidate, or remove content. Regularly performing content pruning helps maintain a high-quality website that meets the evolving needs of your audience.
8. Noindex Page
Before a webpage can appear in search results, search engines like Google need to find and index it.
If you add a "noindex" tag to a page, you're telling search engines not to include that page in their search results. This is useful when you want to keep a page accessible on your website but don't want it to compete with other pages for the same keywords.
To Noindex a Page:
- Include the following line in the <head> section of your page's HTML: <meta name="robots" content="noindex">. This tells search engines not to index the page.
- If the page is listed in your website's XML sitemap, remove it. This helps search engines understand that the page shouldn't be indexed.
If the page has already been indexed by Google, you'll need to request its removal. You have to use Google Search Console for that.
- Log in to your Google Search Console account.
- Navigate to the Removals tool.
- Submit the URL of the page you want to remove from Google's search results.
Following these steps can help you manage which pages of your website appear in search results, helping to prevent internal competition for the same keywords.
9. Keyword Differentiation
Each page on your website should focus on a unique target keyword to avoid competing with other pages for the same search terms. This helps search engines understand what each page is about and increases the chances of higher rankings.
For example, instead of multiple pages trying to rank for "digital marketing," one can focus on "content marketing strategies," while another covers "SEO best practices."
To achieve keyword differentiation, it is important to research keywords carefully. Tools like SEMrush or Google’s Keyword Planner are useful for finding terms that match your content and have good search potential. Giving each page its own specific keyword ensures it meets different user needs, helping you attract a wider audience.
It’s also necessary to review keyword assignments regularly, as search trends and user preferences change over time. Regular content audits can uncover unintentional keyword overlaps and allow adjustments to maintain clarity. Keeping keywords distinct ensures every page serves a specific purpose, improving the overall performance and experience of your website.
10. Content Silos
A content silo organizes a website's content into clear categories or themes, each focused on a specific topic. It includes a main category page that connects to related sub-pages, creating a well-structured hierarchy. This grouping makes it easier for users to find information and helps search engines understand your content better.
Content silos offer several benefits. Users can navigate your website more easily, making their experience enjoyable. Search engines also understand the themes of your content, which can improve keyword rankings. Smart internal linking within silos spreads link value, further boosting SEO.
To build content silos, identify your website’s main topics and split them into smaller subtopics. Create detailed content for each subtopic and link related pages within the same category. This setup not only improves navigation but also strengthens your website's authority on specific topics, leading to better rankings and a smoother user experience.
Preventing Future Content Cannibalization
Preventing content cannibalization is essential to ensure your website's pages don't compete against each other in search engine rankings. Here's how you can avoid this issue:
1. Plan Your Keywords Carefully
Before creating new content, make a list of the keywords you want to target. This helps in assigning unique keywords to each page, preventing overlap. Using keyword research tools can assist in finding relevant and distinct keywords for your topics.
2. Develop a Clear Content Strategy
Outline a content plan that specifies the topics and keywords for each page. This ensures that each piece of content has a unique focus and reduces the risk of duplication. Regularly updating this strategy helps in maintaining clarity as your website grows.
3. Regularly Audit Your Content
Periodically review your website to identify any overlapping content or keywords. Tools like Google Search Console can help in spotting pages that might be competing for the same search terms. Addressing these issues promptly keeps your content distinct and search-engine friendly.
4. Use Internal Linking Wisely
Create internal links that guide users to the most relevant pages. This not only improves user experience but also signals to search engines which pages are most important for certain topics. A well-structured internal linking system supports your overall SEO efforts.
Closing Thoughts
Fixing content cannibalization helps your website work better and rank higher. It’s all about making your content clear, useful, and organized so search engines and visitors enjoy it. Keep an eye on your pages, check for overlap, and update regularly. Small changes like merging similar content or improving links can make a big difference. This isn’t just about SEO—it’s about helping readers find what they need quickly. Think of it like cleaning a messy room; it feels great when everything is in the right place. Start today, and watch your site grow stronger and more user-friendly.
Content Cannibalization FAQs
1. What is content cannibalization in simple terms?
Content cannibalization happens when multiple pages on your website cover the same topic or target the same keywords. This confuses search engines, making it hard for them to decide which page to rank higher, which can hurt your site's visibility.
2. How can I tell if my website has content cannibalization issues?
You might have content cannibalization if you notice several pages on your site competing for the same search terms. Signs include fluctuating rankings for similar keywords or multiple pages appearing for the same search query. Regularly auditing your content can help spot these issues.
3. Why is content cannibalization bad for my website's SEO?
When your pages compete against each other, it dilutes their authority. Instead of one strong page ranking well, you get several weaker ones. This can lead to lower search engine rankings, reduced organic traffic, and a confusing experience for visitors.
4. How can I fix content cannibalization on my site?
To resolve content cannibalization, consider merging similar pages into a single, comprehensive one. Use 301 redirects to guide visitors from outdated pages to the main one. Also, ensure each page targets unique keywords and offers distinct value to your audience.
5. How can I prevent content cannibalization in the future?
Preventing content cannibalization involves careful planning. Develop a clear content strategy where each page focuses on a unique topic or keyword. Regularly review your site's content to ensure there's no overlap, and use tools to monitor keyword usage across your pages.